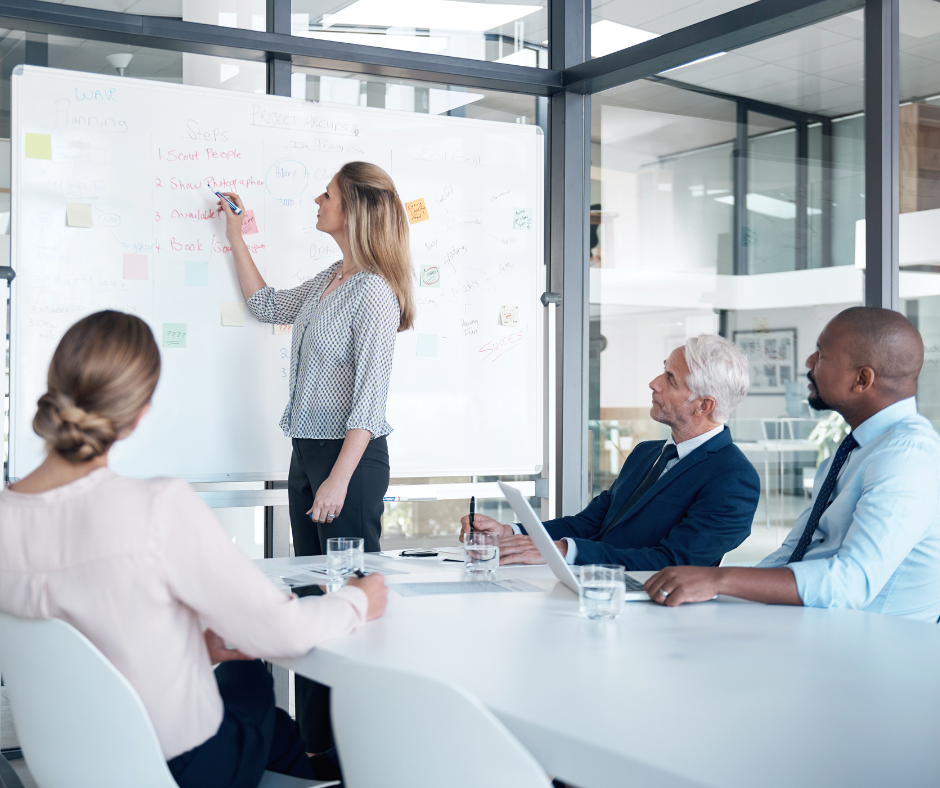
Importance of Project Management
Project management plays a pivotal role in the success of organizations across various industries. It provides structure and clarity by defining objectives, roles, and responsibilities upfront. Clear project goals help teams stay focused and aligned, minimizing misunderstandings and enhancing productivity. Moreover, effective project management enables organizations to anticipate risks and proactively address challenges, thereby increasing the likelihood of project success.
Key Phases of Project Management
A typical project management process consists of several key phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. During the initiation phase, project objectives and stakeholders’ expectations are defined. Planning involves creating a roadmap that outlines tasks, schedules, resource allocation, and budget constraints. Execution is where the actual work of the project takes place, and monitoring and control ensure that the project stays on track.
Skills and Qualities of a Project Manager
Successful project managers possess a diverse set of skills and qualities. They must be adept at leadership, communication, negotiation, and problem-solving. Leadership skills enable project managers to inspire and motivate their teams, while effective communication ensures clarity and alignment among stakeholders. Negotiation skills are essential for managing conflicts and securing resources, while strong problem-solving abilities help in overcoming obstacles and adapting to changes.
Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques support project managers in their roles. Project scheduling software such as Microsoft Project or Trello helps in creating and managing project timelines and tasks. Risk management tools assess potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. Additionally, communication tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams facilitate seamless collaboration among team members, regardless of their geographical locations.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
Project management is not a static process but rather a continuous cycle of improvement and adaptation. Lessons learned from past projects inform future endeavors, allowing organizations to refine processes and enhance outcomes. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, promote iterative development and frequent feedback loops, fostering adaptability in response to changing requirements or market conditions.
In conclusion, effective project management is essential for organizations aiming to achieve their strategic objectives efficiently and effectively. By leveraging structured processes, skilled professionals, and appropriate tools, businesses can navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and deliver successful outcomes in today’s competitive landscape.