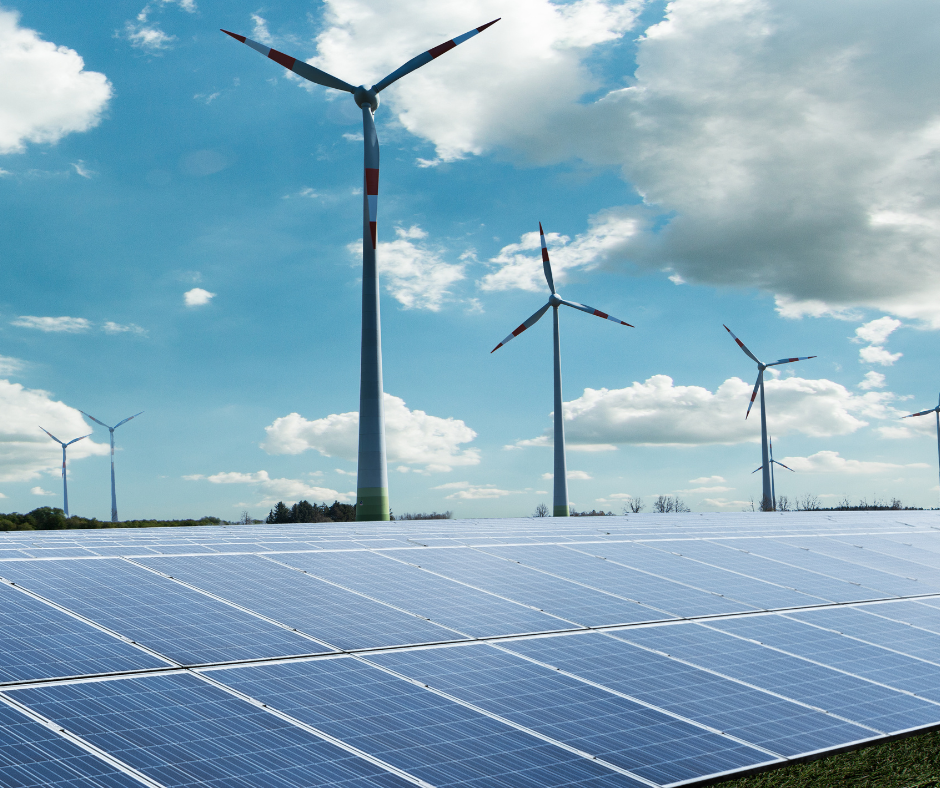
The energy sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences. These trends are reshaping how energy is generated, distributed, and consumed globally. Here are some key trends shaping the future of the energy sector:
Renewable Energy Expansion
There is a notable shift towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power. This transition is driven by increasing environmental awareness, government incentives, and declining costs of renewable technologies. Countries and corporations alike are investing heavily in renewable energy infrastructure to reduce carbon footprints and achieve sustainability goals.
Energy Storage Solutions
The integration of energy storage solutions, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, is gaining momentum. Energy storage addresses the intermittency of renewable sources by storing excess energy generated during peak production periods for use during times of high demand or when renewable sources are not generating power. Advancements in battery technology, coupled with falling costs, are making energy storage economically viable for both grid-scale and distributed applications.
Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grid technologies are enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and resilience of energy infrastructure. These technologies leverage digital communication and automation to optimize energy distribution, monitor grid performance in real-time, and enable two-way communication between utilities and consumers. Smart grids support integration of renewable energy sources, facilitate demand response programs, and improve grid stability against disruptions.
Electrification of Transportation
The electrification of transportation, driven by electric vehicles (EVs), is transforming the energy landscape. EV adoption is accelerating globally due to advancements in battery technology, government incentives, and growing consumer interest in sustainable transportation options. This trend is creating opportunities and challenges for energy utilities to manage increased electricity demand from charging infrastructure while supporting grid reliability and stability.
Energy Efficiency and Demand-Side Management
Energy efficiency initiatives and demand-side management strategies are becoming integral to energy sector planning. Governments, businesses, and consumers are prioritizing energy conservation measures to reduce energy consumption, lower operating costs, and minimize environmental impact. Technologies such as smart meters, energy-efficient appliances, and building automation systems are instrumental in optimizing energy use and promoting sustainable practices.
Decentralization and Energy Independence
There is a growing trend towards decentralization of energy generation through distributed energy resources (DERs) such as rooftop solar panels, microgrids, and community-based renewable energy projects. Decentralization promotes energy independence, enhances grid resilience, and empowers consumers to generate, store, and manage their own energy. This trend is reshaping traditional utility business models and fostering a more diversified, resilient energy ecosystem.